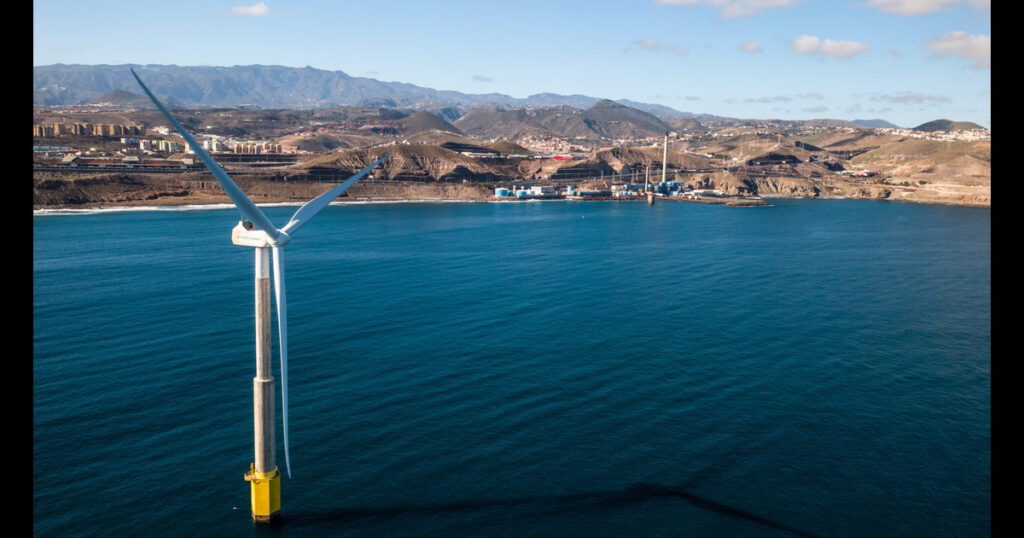
Hydrogen energy is increasingly recognised as a key pillar in the global transition towards clean and sustainable energy systems. As the world strives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, green hydrogen offers a promising solution. Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen can provide energy with zero carbon emissions when produced from renewable sources. This positions hydrogen not just as a viable alternative for today, but the energy of the future.
What is Green Hydrogen?
As we mentioned in our previous blog articles on H2Heat, Green hydrogen is produced via electrolysis, where renewable electricity — such as wind or solar power — is used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process emits no carbon dioxide, different from grey or blue hydrogen which rely on fossil fuels. The result is a clean energy carrier capable of powering industries, heating, transport, and even storing energy to balance supply and demand in electricity systems.
Trends in Hydrogen Energy Utilisation (2025)
As of 2025, there is escalating momentum globally around hydrogen energy, driven by policy support, technological advancements, and large-scale projects. Significant investment has been made in infrastructure development, electrolyser technologies, and hydrogen fuel cells. Many sectors are actively exploring hydrogen adoption, particularly where decarbonisation is challenging with existing technologies. These include heavy industries, long-haul transportation, power generation, and notably, heating for commercial and residential buildings.
Challenges remain with high costs of production and infrastructure.
However, challenges remain, primarily the high costs of production and infrastructure, and the need for scaling electrolyser technology and transport systems. The hydrogen sector is rapidly evolving with an aim to overcome these hurdles and to establish hydrogen as a mainstream, climate-neutral energy carrier.
Here is the continuation with the section on advantages of hydrogen energy and introduction to the H2Heat Project:
The Advantages of Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen energy stands out with several key benefits that are driving its emergence as a future energy source in 2025:
- Zero emissions at point of use: Hydrogen combustion produces only water vapour, making it a truly clean energy carrier with no carbon dioxide emissions. This makes a significant contribution to fighting climate change and improving air quality.
- Versatility: Hydrogen can be used in multiple sectors including heavy industry (such as steel and chemical production), transportation (fuel cell vehicles, trucks, buses, even aircraft), energy storage, and heating for buildings.
- Energy security and independence: By enabling countries with renewable energy resources to produce their own hydrogen, reliance on imported fossil fuels can be reduced, enhancing energy independence.
- Economic opportunities: The development of hydrogen infrastructure and technologies is creating new jobs and growth in clean energy industries.
- High energy efficiency and reliability: Hydrogen fuel cells offer higher efficiencies compared to traditional internal combustion engines and power plants. Their modularity and scalability allow them to support diverse energy needs, including for remote or off-grid communities.
- Energy storage and grid balancing: Hydrogen effectively stores excess renewable electricity, enabling smoothing of energy supply and providing backup power, which helps overcome the intermittency of renewables.
Despite these advantages, hydrogen energy faces challenges primarily related to costs and infrastructure development. Production of green hydrogen via electrolysis is still relatively expensive, although costs are steadily decreasing with technological innovation and scale-up. Building out hydrogen transport, storage, and refuelling infrastructure also requires significant investment.
The H2Heat Project: Driving Forward Hydrogen for Heating
A leading example of hydrogen’s potential in commercial heating is the H2Heat Project based in the Canary Islands. Coordinated by the Oceanic Platform of the Canary Islands (PLOCAN) in collaboration with the Canary Island Health Service (SCS), the project aims to demonstrate the full value chain, from renewable energy generation offshore, green hydrogen production, to its use in heating large commercial buildings such as hospitals.
The project leverages offshore wind energy to power state-of-the-art electrolyser technology to produce high-purity green hydrogen. This hydrogen feeds into innovative combined heat and power (CHP) systems and hydrogen heat pumps that provide heating energy to the CHUIMI hospital complex in Gran Canaria.
H2Heat’s objectives include:
- Reducing CO2 emissions by more than 50% in hospital heating,
- Demonstrating cost efficiencies and technology readiness for commercial scalability,
- Providing a replicable model to be scaled to other hospitals and tourism sectors across the Canary Islands,
- Enhancing energy autonomy for islands traditionally reliant on imported fossil fuels,
- Integrating community engagement and education via its quadruple helix model involving government, industry, researchers, and civil society.
By advancing technology readiness levels (TRL) and successfully integrating hydrogen into real-world heating applications, H2Heat offers a blueprint for accelerating the hydrogen economy beyond the Canary Islands, supporting EU climate goals, and illustrating hydrogen’s vital role in the future clean energy landscape.
References
- H2Heat Project. (2025). Here is Why Hydrogen is the Future of Clean Energy.
- H2Heat Project. (2025). Hydrogen Benefits and Considerations. U.S. Department of Energy Alternative Fuels Data Center.
- Montel Energy. (2025). What Are the Benefits of Hydrogen for Net-zero?
- Bloom Energy. (2025). What are the Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
- H2Heat Project. (2025). Dissemination and Communication Plan D7.1