
How can Hydrogen Power a House?
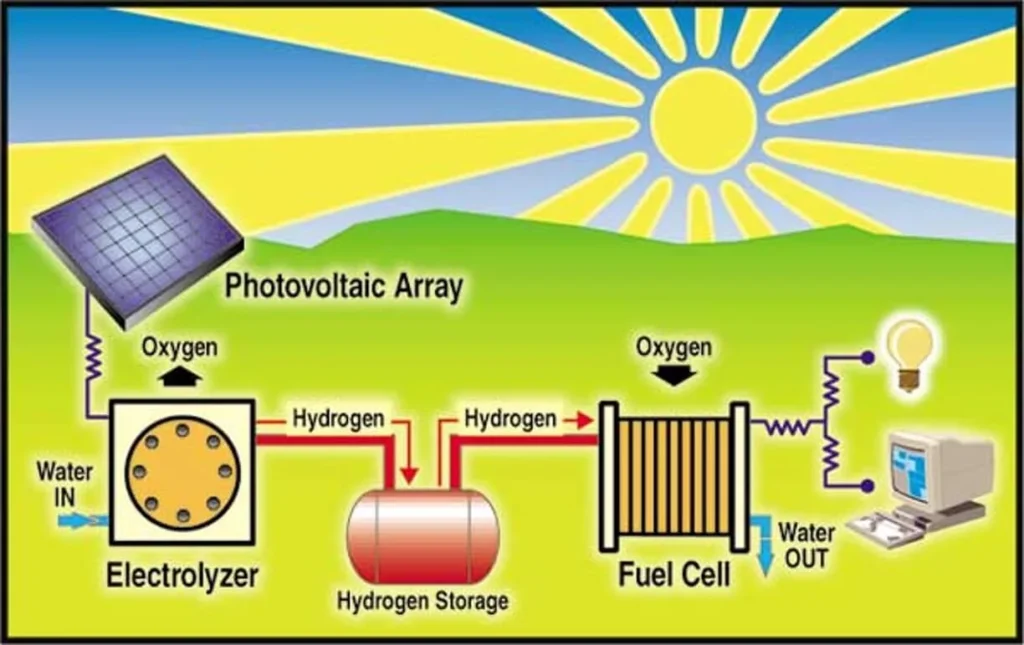
How can Hydrogen Power a House? https://h2-heat.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/johnson-johnson-U6Q6zVDgmSs-unsplash-2-1024x768.jpg 1024 768 H2Heat Project https://h2-heat.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/johnson-johnson-U6Q6zVDgmSs-unsplash-2-1024x768.jpgIn a household, a hydrogen fuel cell system converts stored hydrogen into electricity and heat through an electrochemical reaction that combines hydrogen with oxygen. This process releases energy in the form of electricity, which recharges the batteries and powers the home’s appliances. Remarkably, the only byproduct of this reaction is water, which can be recycled to generate more hydrogen, initiating the cycle again. This efficient process provides both electricity and heat, making it a valuable energy source for residential use.
Hydrogen Blending
According to Nationalgrid.com Hydrogen blending involves mixing hydrogen with natural gas to reduce emissions, as transitioning to 100% hydrogen isn’t currently feasible. This is due to ongoing developments in hydrogen production infrastructure and differences between hydrogen and methane gases, such as their flow characteristics. Testing is necessary to evaluate how existing gas pipeline networks perform when hydrogen is introduced.
Scientists are experimenting with blending hydrogen with natural gas to achieve emission reductions, as this approach requires less natural gas. Hydrogen is injected into the natural gas system, resulting in a mixture or ‘blend’ of natural gas and hydrogen. This method serves as a transitional solution while advancements in hydrogen infrastructure continue to evolve.
Introducing Hydrogen into Homes
To introduce clean hydrogen gas into our homes, it’s crucial to ensure that household appliances such as boilers, cooking appliances, and gas fires are compatible with hydrogen. Manufacturers have already developed hydrogen boilers, indicating that the technology exists – it just requires a widespread strategic transition, led centrally by the government.
Similar to the transition from analogue to digital TV, preparations can be made in anticipation of the shift in our heating systems to make the transition as smooth and seamless as possible. One approach could involve mandating that all new gas boilers installed be hydrogen-ready, ensuring a seamless transition when the time comes to switch to hydrogen.
Experts are optimistic about the timeline, anticipating that the shift to hydrogen heating will commence within the next decade, aligning with the targets set by the UK and US governments to significantly reduce carbon emissions by 2035. In the US, the Department of Energy has launched the Hydrogen Earthshot initiative, aiming to reduce the cost of hydrogen to $1 per kilogram within one decade.
The promising aspect is that hydrogen can be transported through existing gas networks and stored using conventional technology. This presents a cost-effective solution, minimizing the need for expensive new infrastructure for hydrogen transmission and distribution networks while also reducing disruption.
Currently, hydrogen blending trials are underway to determine the feasibility of incorporating hydrogen into existing pipelines, offering insights into the potential use of hydrogen in our existing infrastructure.
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen can be produced through electrolysis, a process where electricity is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Alternatively, hydrogen can be derived from natural gas through steam methane reforming (SMR), albeit with carbon emissions.
Storage
Produced hydrogen is stored in tanks or cylinders at the home, providing safe and efficient storage for on-demand use.
Fuel Cells
A hydrogen fuel cell system installed in the house converts stored hydrogen into electricity and heat. Combining hydrogen from storage tanks with oxygen from the air, fuel cells generate electricity, heat, and water vapor as byproducts. The electricity powers the home’s appliances, while the heat can be used for water heating or space heating.
Powering the House
Electricity generated by the hydrogen fuel cell system lights up the home and powers appliances and electronics. Heat produced by the fuel cell can be utilized for domestic water heating or space heating, especially during colder seasons. Excess electricity can be stored in batteries or fed back into the grid for later use or to offset energy costs.
Benefits
- Clean Energy: Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity without emitting harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases, making them a clean and environmentally friendly energy source.
- Energy Independence: By generating electricity on-site using hydrogen fuel cells, homeowners can reduce their dependence on the grid and fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and resilience.
- Efficiency: Hydrogen fuel cells are highly efficient, converting chemical energy directly into electricity with minimal waste heat, resulting in lower energy consumption and operating costs compared to traditional combustion technologies.
- Quiet Operation: Hydrogen fuel cells operate quietly and produce minimal noise, providing a silent and reliable power source for residential applications.
Considerations
- Cost: While hydrogen fuel cell technology offers numerous benefits, the initial cost of installation and equipment can be high. However, ongoing advancements and increased adoption of the technology may lead to cost reductions over time.
- Infrastructure: Currently, hydrogen infrastructure, including production, storage, and distribution, is limited in many areas, which may pose challenges for homeowners interested in adopting hydrogen energy for residential use.
- Safety: Proper handling and storage of hydrogen are essential to ensure safety, as hydrogen is highly flammable and requires careful management to prevent accidents or leaks.