H2Heat Plans and Prepares for Transformation, #Now is the time
H2Heat Plans and Prepares for Transformation, #Now is the time https://h2-heat.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/image0_0-7-2.jpg 1024 1024 H2Heat Project https://h2-heat.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/image0_0-7-2.jpgThe planning and preparation phase of the H2HEAT project is a vital step in bringing this transformative vision to life. In this blog post, we will delve into the project’s objectives, key tasks, and the remarkable journey that lies ahead.
Setting the Stage of H2Heat
The H2HEAT project’s planning and preparation is driven by a set of core goals, each essential for its successful execution:
1. Overall Detailed Project Plan
At the heart of the project lies a crafted plan that not only outlines the journey ahead but also provides a detailed budget and a timeline that keeps everyone aligned and accountable.
2. Consenting and Permitting
Every significant endeavor requires the green light from the powers that be. H2HEAT is committed to securing all the necessary permissions and consents to ensure a smooth and lawful progression.
3. Environmental Impact Assessment
With a strong emphasis on environmental responsibility, H2HEAT conducts a comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). Continuous monitoring is part of the commitment to minimize ecological harm.
4. Resource and Demand Forecasting
Efficiency is key, and that’s why the project meticulously analyzes and forecasts energy demand, ensuring resources are used optimally.
5. Site Survey and Techno-Economic Analysis
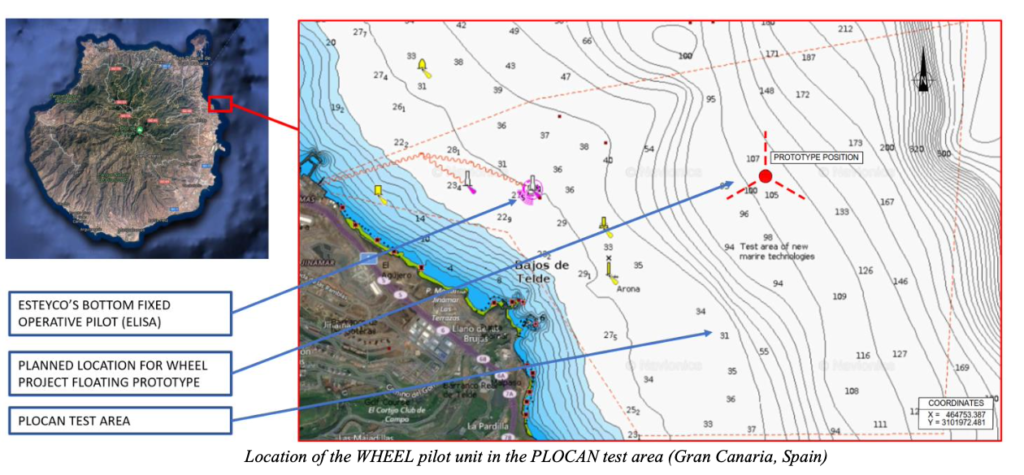
To maximise efficiency and performance, H2HEAT partners with PLOCAN to evaluate the suitability of the project site. Detailed techno-economic analysis guarantees an optimized configuration.
6. Health & Safety Strategy
Safety is a top priority. A thorough Health and Safety (H&S) strategy is developed and executed, covering all aspects of the project to protect the well-being of the team.
Tasks at Hand: Driving Sustainability
Let’s zoom in on the specific tasks that are steering the H2HEAT project towards success:
Project Planning: The project plan is not static; it’s continuously reviewed and updated as progress is made. A detailed budget is created based on a techno-economic analysis and project requirements.
Consenting and Permitting: This task involves obtaining a range of permits, including administrative authorisation, environmental assessments, and manufacturing licenses. The project also explores the possibility of grid connection if needed.
Site Surveys and Resource Assessment: Evaluating the project site near Las Palmas Gran Canaria is crucial. Historical weather data and energy demand forecasts guide decision-making.
CHUIMI Hospital Analysis: A comprehensive review of CHUIMI hospital’s heat requirements is conducted, ensuring that the project aligns with current usage, seasonal variations, and equipment needs.
Preliminary Designs and Specifications: A high-level system design study is carried out, covering renewable energy sources, electrolysis, infrastructure, hydrogen production, and heat distribution. This study helps optimize the system layout and estimate costs.
Environmental and Permitting Activities: This task encompasses a full Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), administrative procedures, and measures to mitigate environmental impact. Ongoing environmental surveillance is also established.
Health and Safety (H&S) Plan: Safety is paramount. A comprehensive H&S plan includes risk assessment, scenario development, emergency procedures, personnel designation, and a training and communication plan.
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA): A standardized methodology is used to assess the project’s impact on environmental and socio-economic factors, including circularity and the project’s location.
Environmental Impact Monitoring and Reporting: The project continuously monitors its supply chain, tracking progress in reducing carbon emissions and reporting on compliance with the EIA baseline report.
The H2HEAT project is not just about innovation; it’s about pioneering a sustainable and eco-conscious future.


