On the horizon, a significant event is set to unfold—the H2Heat project kick-off meeting, scheduled for the 27th of September. This three-day event promises to mark the beginning of a journey towards a sustainable energy future. With 11 project partners forming a consortium, the H2Heat project aims to make a lasting impact on the energy landscape.
The 11-Partners Project
At the heart of the H2Heat project are 11 project partners, united by a shared vision for a greener, more sustainable future. This consortium, comprising experts from various fields, will collaborate closely to bring innovative solutions to the forefront of sustainable energy.
The Power of Connectivity: Zooming into the Meeting
In the age of digital connectivity, the H2Heat kick-off meeting is set to harness the power of the internet. Held live via Zoom with Link, this meeting will be accessible to anyone interested in the project’s mission.
Unveiling Work Packages: Responsibilities in Focus
One of the highlights of the kick-off meeting will be the presentation of Work Packages by each partner. These Work Packages serve as the blueprints for the project’s success, outlining each partner’s unique responsibilities and contributions. This transparency ensures that everyone is on the same page, fostering collaboration and synergy among the partners.
Timing is Everything
The kick-off meeting will adhere to the Western European Summer Time (WEST) timezone, commencing at 09:30 and concluding at 18:30. This well-structured schedule ensures that every minute of the three-day event is utilized efficiently, as the project partners embark on this transformative journey.
At its core, the H2Heat project carries a grand ambition. Boasting a budget of 13 million euros, of which a substantial 10 million euros is generously provided by the European Union, and spanning a duration of five years, its overarching goal is to demonstrate the entire value chain of green hydrogen (H2) utilization for heating purposes within commercial buildings. These structures collectively account for 40% of the total energy consumption and a significant 36% of greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union. Remarkably, a staggering 79% of this energy demand is attributed to water heating and air conditioning.
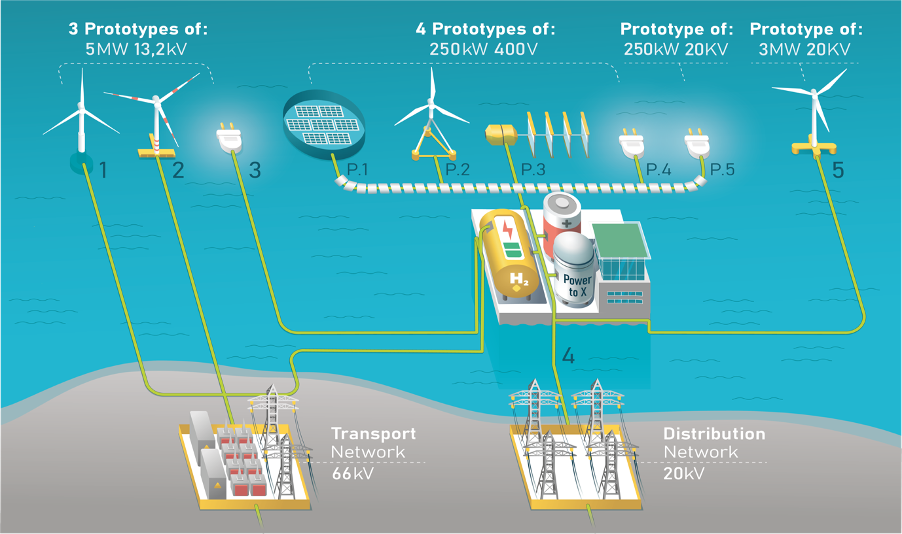
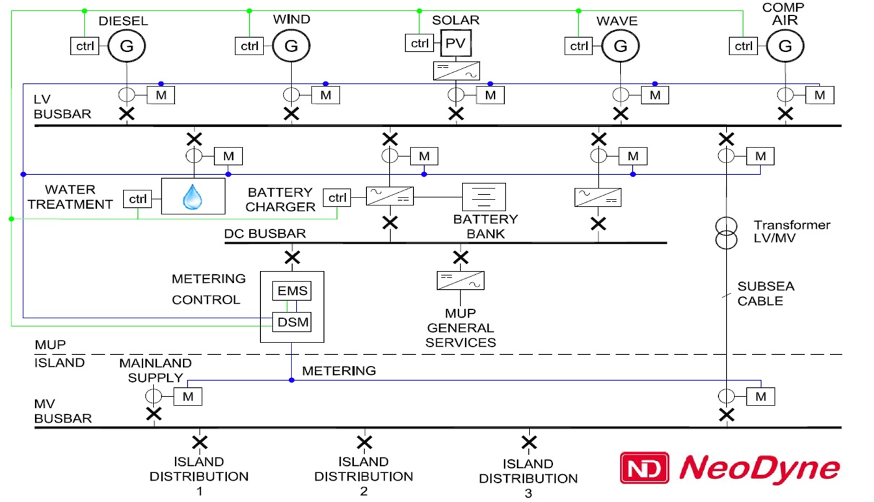
The H2Heat project, officially titled “Innovative Production of Renewable Energy Vectors for Heating from Renewable Energy” introduces several pioneering elements. These include the production of highly combustible hydrogen through an innovative 1MW electrolyzer that utilizes marine renewable energy sources. Additionally, the project combines advanced combustion technology in the form of a hydrogen-operated Combined Heat and Power (CHP) burner, as well as a heat pump. These innovative components are complemented by a robust infrastructure designed to transport hydrogen from the production facility to the end-user.
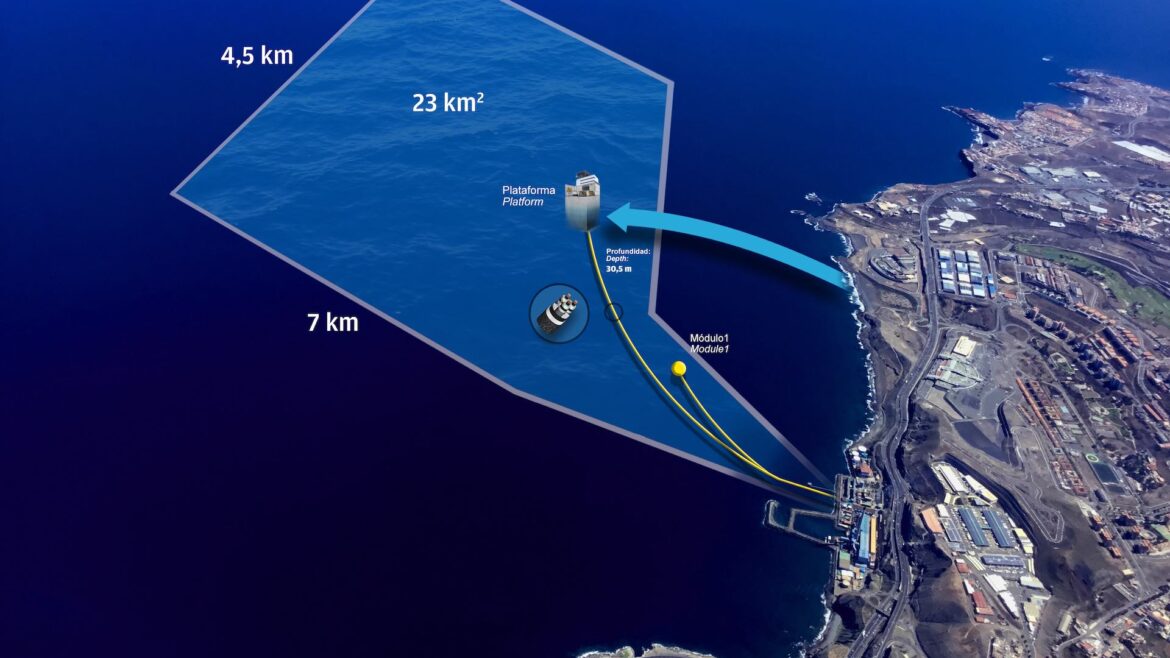
The source of renewable energy for this endeavour will be Esteyco’s offshore wind turbine. The electrolyzer will find its home at EMALSA’s facilities in Jinámar, while the CHP burner and heat pump will be stationed at the Complejo Hospitalario Insular Materno Infantil de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (CHUIMI).
Zero Net Emissions Health Strategy
In a significant stride towards sustainability, H2HEAT collaborates closely with the Canary Health Service (SCS) to create a comprehensive demonstration of green hydrogen for heating and subsequent energy applications. This demonstration model will serve as a blueprint for all SCS hospitals, enabling the fulfillment of the “Zero Net Emissions Health Strategy.” This strategy entails a profound decarbonization effort, positioning the project as a trailblazer in shaping a “Hydrogen Valley” concept on the island of Gran Canaria, with future expansion plans encompassing the entire archipelago.
The collaborative expertise within the consortium ensures the efficient realization of the project’s technical objectives. It aims to substantially reduce the cost of H2 fuel for consumers and develop scalable business models for extensive commercial utilization of hydrogen as a primary heating alternative in Gran Canaria.
The esteemed partners comprising the H2Heat project consortium are as follows: PLOCAN; Esteyco Spain, specialising in fixed and floating wind turbine technology; Neodyne Ireland, responsible for electrical engineering and EMS control; Stargate Estonia, overseeing the electrolyzer, compressor, and storage; 2G Spain, in charge of H2 CHP technology; ICoRSA Ireland, contributing to Dissemination and Communication, as well as Public Engagement; CMS Spain, leading public engagement efforts in Gran Canaria; EMEC UK (Orkney Islands), providing invaluable experience in H2 distribution networks, business models, and techno-economics; SCS/CHUIMI Spain, representing the Canary Health Service; Canary Islands Agency for Research, Innovation, and Information Society of the Canary Islands Government (ACIISI); and SPLP Ukraine, renowned H2 experts specialising in electrolyzer research.
With global access via Zoom, a stunning location, and meticulous planning, this event has all the elements to set the stage for a brighter, cleaner energy future. Stay tuned for updates as the H2Heat project unfolds and leads the charge towards a greener world via our X (f.k.a. Twitter) and LinkedIn.